In the ever-evolving landscape of digital commerce, the integration of generative AI promises to revolutionize the roles of marketers and merchandisers. As businesses increasingly adopt AI technology, it’s important to understand the profound impact on job dynamics within the ecommerce sector. This article delves into the transformation brought about by generative AI and explores the changing nature of tasks, the challenges businesses face, and the pivotal role of leadership in embracing this technological shift.
How AI Can Help Marketers and Merchandisers
With generative AI opening up new avenues for innovation, it’s having a significant impact on the evolution of ecommerce jobs and workflows.
It also begs the question: How is generative AI impacting the day-to-day of those working in our industry? And what are the implications?
Increased Productivity and Time Savings
By driving productivity and removing manual tasks that stand in the way of more valuable work, generative AI will offer new ways to use our minds and our time.
Generative AI is akin to the washing machine of the digital era, saving not only manual labor but also mental labor. The technology enables the outsourcing of low-level decision-making and judgment, transforming tasks from multi-threaded to single-threaded processes.
To illustrate this further, there are a number of ways in which generative AI acts as a personal assistant, limiting the routine work of marketers and merchandisers and allowing their time to be better spent on work that has higher business impact and value.
For example:
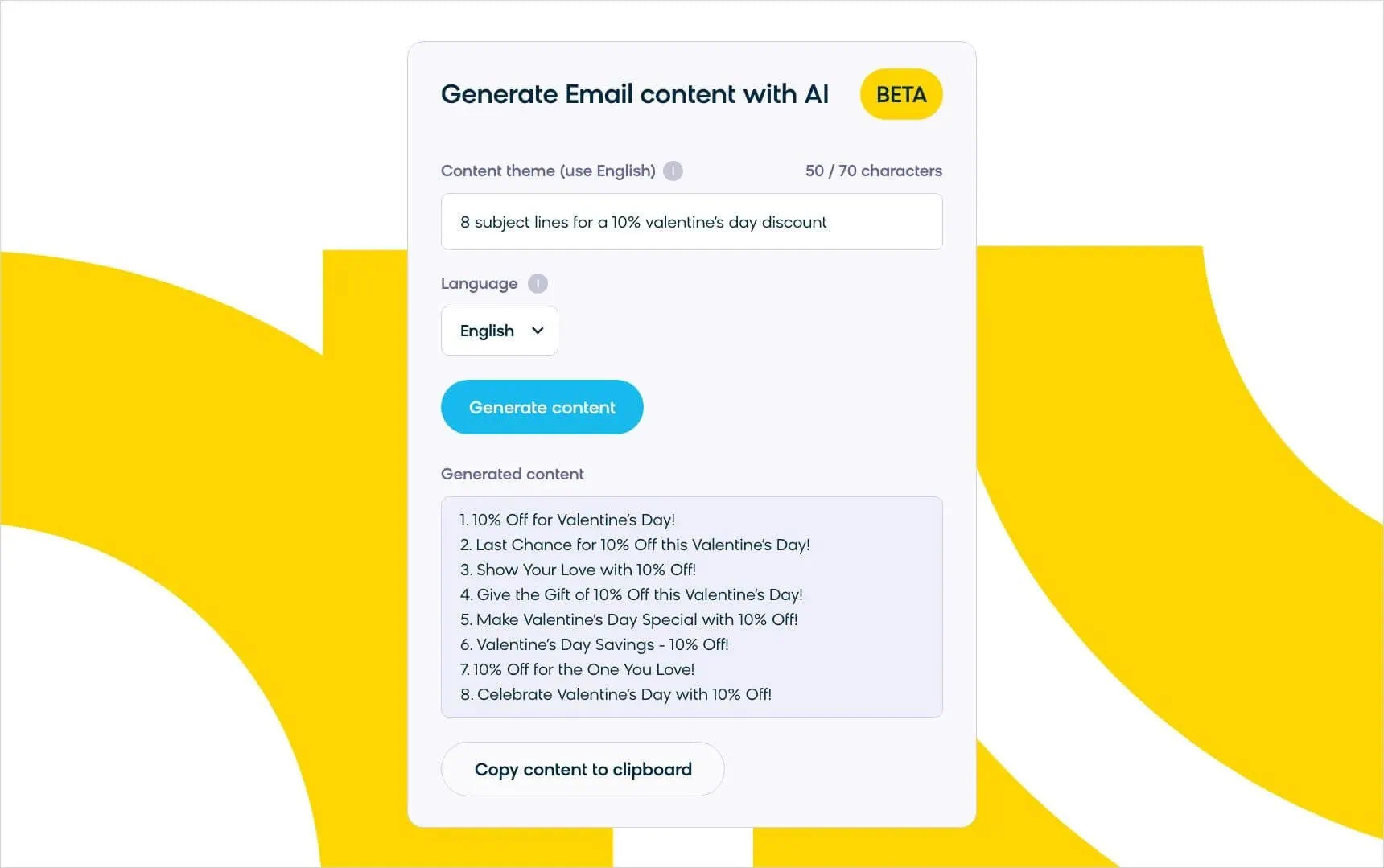
- Content creation: Marketers can use AI to create personalized email, SMS, and even site content quickly — and at scale.
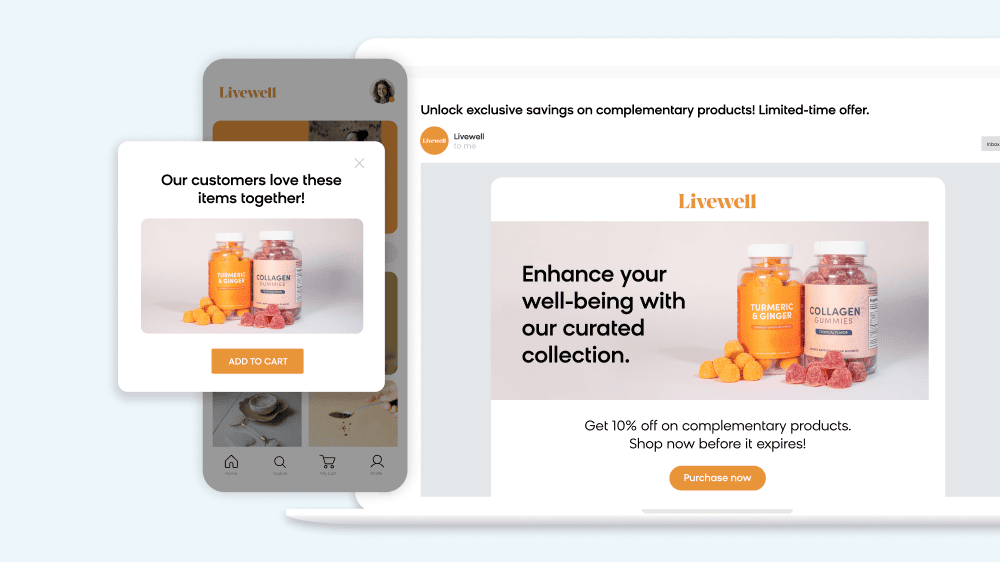
- Customer journeys: This involves using AI predictions to determine what email or SMS should come next in a flow, what promotion to offer, when to send it, and more.
- Merchandising: AI can be used to generate extensive lists of product synonyms or group similar products.
- Testing: AI can go beyond traditional A/B testing and send personalized variants to each customer.
In this way, generative AI frees up time for ecommerce professionals, allowing them to redirect their cognitive abilities toward more strategic and creative pursuits.
Faster Content Creation and Better Personalization
Generative AI will allow for faster content creation across marketing and merchandising — and that will enable more and better personalization.
One of the immediate benefits of generative AI is the acceleration of content creation. The ability to create, iterate, and test message variants at scale facilitates better personalization. This not only enhances the efficiency of marketing efforts but also provides a competitive edge in delivering tailored experiences to consumers.
When it comes to personalization, there is a hidden challenge that is not always discussed: What content assets are you going to apply that personalization to?
The more granular your segmentation and the more advanced your personalization goals, the more content you need. Even just multiple variations of web banners, product images, email copy, and email content are often too laborious and time-consuming for many organizations to create. Most ecommerce businesses struggle to get one version of everything done in time with the resources they have (and can afford), let alone many.
Generative AI will allow digital commerce teams to create and test these content variations at scale — quickly and easily. It will allow them to move toward a level of personalization that simply wasn’t possible before because they’ll now have endless assets to which they can apply that personalization.
With Gartner predicting that 80% of creatives will use generative AI on a daily basis by 2026, we may also end up seeing increased spending on creative. The use of generative AI in marketing will enable more creative variations for hyper-targeted, personalized experiences. In order to manage all of this, a knock-on effect might be an increase in CMO spend on agency and in-house creative talent.
The Human Will Have More Say
By automating routine, menial tasks, generative AI empowers marketers and ecommerce professionals to have a more profound impact on processes and campaigns.
This shift allows individuals to focus on higher-level thinking and strategic decision-making, emphasizing creativity and innovation. The collaboration between humans and AI becomes a symbiotic relationship, drawing on the strengths of both. For example, if you tell your generative AI tool your priorities, it will use that information to make recommendations and suggest the best course of action when it makes sense.
When it comes to the integration of generative AI within marketing and ecommerce workflows, it’s therefore not a push-or-pull scenario, but more a case of hand-in-hand collaboration.
Challenges and Considerations
The transition to generative AI is not without challenges, though. Let’s take a look at what some of these could be.
Overcoming Hesitancy
While AI is all the buzz right now, some businesses are still hesitating to adopt the technology, fearing the need to rebuild existing processes and workflows. Copywriters and practitioners, in particular, might express concerns not about job replacement but about the perceived erosion of their value. It’s important that your leadership team understands and addresses these fears to successfully integrate generative AI into marketing and ecommerce processes.
They can start by understanding the value those team members bring and reframing the conversation. For example, positioning AI as a way for teams to “spend more time on the fun or important stuff” can be a useful starting point in overcoming hesitancy. Another consideration is to ask team members to make a list of all the things they don’t want to do and use that as a basis for finding ways to use AI to tackle those tasks.
In some ways, the hesitancy is reminiscent of the early days of ecommerce. There was a time when people felt very strongly that the physical store had to be the business focus. To get around this concern, business leaders should look at how generative AI improves the overall experience for marketers and merchandisers. Once you start optimizing for whatever KPI or metric is important to your team, you can help those who are resistant to change to learn and get on board with the transformation.
Shifting Culture
Building on the hesitancy many businesses face with AI, there’s also the matter of adjusting the company’s culture to embrace AI adoption. After all, the technology represents a potentially big shift in how employees handle their day-to-day workload — any culture shift requires a careful balance between strategic alignment and manageable risk.
Employers need to evaluate the impact of generative AI on productivity, creativity, and personalization in this new landscape. It’s also important to consider how this might change the role of professionals, as well as traditional work schedules and talent acquisition strategies. For example, could the productivity gains from generative AI result in a four-day workweek? Does a new strategy-focused workload still leave room for work-life balance? Should you start prioritizing AI experience in new hires or include AI training as part of onboarding?
For AI technology to reach its full potential, companies will need to make sure they make AI a priority and focus across the entire company.
Knowing How To Start
Companies often struggle with determining where to begin, especially in the face of the technology’s inevitable hiccups. Organizations may cautiously begin with tasks like content generation, but the leap to more complex applications raises concerns. It’s crucial to identify use cases that align with current initiatives rather than treating AI adoption as a mere science experiment. This will require asking questions like: What are you actually trying to get out of it? What’s the use case? What problem are you trying to solve?
The journey to generative AI integration requires rebuilding existing processes, finding the time and resources, and, for large corporations, navigating the intricacies of risk management.
Finding the Right Approach With Generative AI
So, what should businesses be mindful of regarding generative AI and its application within marketing and ecommerce roles?
Here are 3 key considerations for businesses:
Making an Impact
Companies should strategically assess where they can make the most significant impact with generative AI. Identifying sensitive and affectable points on the customer experience journey is essential. The use cases must ladder up to current initiatives, ensuring scalability without disrupting the brand. This approach will help you avoid the pitfalls of treating generative AI as a mere add-on or experimental project.
Balancing Risk and Innovation
The fear of high risk often prevents businesses from integrating technology with key business initiatives. That’s why it’s important to strike a balance between strategic alignment and manageability. Companies need to choose use cases that align with their KPIs, providing a clear path to success while gradually integrating generative AI into their operations.
Keeping the Human in the Loop
AI should be seen as a collaborative tool, not a replacement. It might be helpful to think of it in terms of “AI as your first draft,” complementing and augmenting human capabilities.
For example, embracing generative AI for marketing content creation, writing product descriptions, or any number of other use cases still remains difficult to do in a brand-friendly way. It’s still going to require people to moderate, iterate, and further train models. This means the skills the best copywriters need today will transition from creation to editing, curating, and quality control. This is no different for marketers and merchandisers than it is for software developers. ChatGPT might be able to write code, but would you risk implementing that without QA? And don’t you need someone to do the implementation itself?
Marketers and ecommerce professionals should therefore communicate their priorities to the AI, allowing it to assist and suggest solutions while maintaining the human touch in decision-making.
In this way, generative AI isn’t going to necessarily replace roles, but it will change them. This will require an adjustment for some, but it will enable professionals to reclaim their time for projects that have been on the back burner and never see the light of day due to a lack of time and resources.
Using Generative AI To Evolve Our Jobs
As generative AI reshapes the landscape of ecommerce, companies must navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities it presents. The key lies in demonstrating how generative AI enhances the overall customer and employee experience. By optimizing for specific metrics and KPIs, businesses can focus their efforts, as well as help the workforce overcome resistance and learn to use AI for the benefit of all.
Generative AI is a catalyst for driving productivity, fostering innovation, and redefining marketing and ecommerce roles. By understanding the challenges, finding the right approach, and embracing a culture of collaboration with humans working in tandem with machines, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of this seismic shift happening in our industry.
If you’re curious how Bloomreach is powering the next wave of limitless marketing using the latest advancements in generative AI, learn more about Loomi, our AI built for ecommerce, and Bloomreach Clarity, our innovative conversational shopping solution.